Direct Vs Indirect Labor Cost: An Expert Accounting Guide
Later in Part 6 we will discuss what to do with the balances in the direct labor variance accounts under the heading What To Do With Variance Amounts. Of the total amount, the company needs to account for the payroll taxes of $15,000 while the rest of $85,000 will go to the wages payable. Mostly, these costs are mainly concerned with the production process, and therefore, they are variable in nature. Varying from industry to industry, they are treated on a product basis (in a manufacturing concern), or a client basis (in the service sector). Rookwood Pottery makes a variety of pottery products that it sells to retailers. Accounts Payable is a liability account that represents bills that are due for purchases and other costs of doing business, and the Raw Materials account is an asset that represents materials on hand.
Applied Manufacturing Overhead to All Production Departments
These are especially significant in businesses with high human resource labor expenses, such as construction, manufacturing, and other partially or fully automated activities. This example only deals with one employee, but you can scale it up to accommodate as many employees as you have participating in manufacturing products or providing services. If a three-person auditing team spends a full 40-hour work week auditing a client's inventory, that equates to 120 hours of labor on that job -- three auditors times 40 hours worked each. John Freedman's articles specialize in management and financial responsibility. He is a certified public accountant, graduated summa cum laude with a Bachelor of Arts in business administration and has been writing since 1998. His career includes public company auditing and work with the campus recruiting team for his alma mater.
Why Use a Predetermined Overhead Rate?
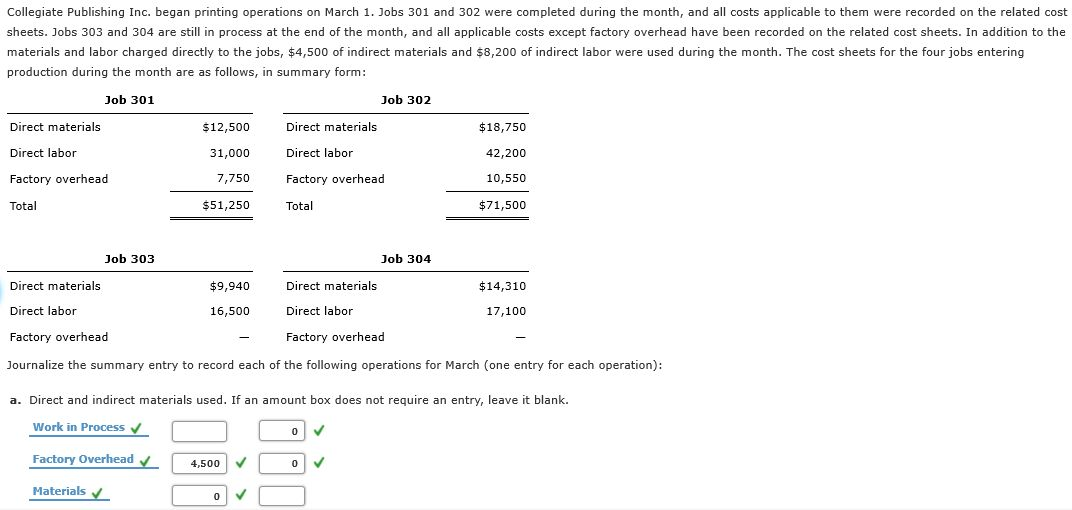
Direct labor is the total cost of wages, payroll taxes, payroll benefits, and similar expenses for the individuals who work directly on manufacturing a particular product. The direct labor costs for Dinosaur Vinyl to complete Job MAC001 occur in the production and finishing departments. In the production department, two individuals each work one hour at a rate of $15 per hour, including taxes and benefits. The finishing department’s direct labor involves two individuals working one hour each at a rate of $18 per hour.
Using a Manufacturing Overhead Account
- The total job costof Job 106 is $27,950 for the total work done on the job, includingcosts in beginning Work in Process Inventory on July 1 and costsadded during July.
- This entry accounts for the funds owed to the company and the recording of sales.
- When manufacturing overhead is applied to the jobs in process, it is credited from the Manufacturing Overhead account and debited to the Work In Process account.
- It is one of the significant components of the product cost of the company where the other components of the product cost include direct material cost and manufacturing overhead costs.
These property taxes are considered indirect manufacturing costs and should be applied to all jobs produced during the year and not just the jobs in process at the time the taxes are paid. In traditional costing systems, the most common activities used as cost drivers are direct labor in dollars, direct labor in hours, or machine hours. Often in the production process, there is a correlation between an increase in the amount of direct labor used and an increase in the amount of manufacturing overhead incurred.
Along with these direct materials and labor, the project will incur manufacturing overhead costs, such as indirect materials, indirect labor, and other miscellaneous overhead costs. In some cases, organizations choose not to use a single, organization-wide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate to apply manufacturing overhead to the products or services produced. In the preceding sections, an organization-wide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate was calculated. Many organizations have multiple departments or processes that consume different amounts of manufacturing overhead resources at different rates.
Transferred Goods from the Packaging Department to Finished Goods
Furthermore, these charges are critical to comprehend for any organization for a smoother labor working process. In this journal entry, the amount of the labor cost usually includes both direct labor cost and indirect labor cost. The costs for direct labor is debited to the Work In Process inventory account and indirect labor is debited to the Manufacturing Overhead account. Direct labor costs are manufacturing labor costs that can be easily and economically traced to the production of the product. Indirect labor costs are manufacturing labor costs that cannot be easily and economically traced to the production of the product, e.g. the production supervisor’s salary or quality control. Organizations that produce unique or custom products or services typically use a job-order costing system.
The raw materials inventory department maintains a copy to document the change in inventory levels, and the accounting department maintains a copy to properly assign the costs to the particular job. The Raw Materials inventory account is used to record the costs for all raw materials—direct and indirect—purchased to manufacture a product. Exhibit 2-3 Formula for organization-wide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate. The formula for computing an organization-wide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate is presented in Exhibit 2-3. The word ‘labor costs’ refers to the overall cost of all labor, which is a crucial aspect of any business. Furthermore, labor costs work as one of the main significant operating costs.
The company can make the labor cost journal entry by debiting the labor cost account and crediting wages payable account and payroll taxes payable. In accounting, labor cost journal entry will start how to calculate predetermined overhead rate: formula and uses with the period-end adjusting entry when the company needs to accrue the wages payable for the period. Later on, the company will need to assign the labor cost to appropriate manufacturing accounts.
The total job costof Job 106 is $27,950 for the total work done on the job, includingcosts in beginning Work in Process Inventory on July 1 and costsadded during July. This entry records the completion of Job 106 bymoving the total cost FROM work in process inventory TO finishedgoods inventory. Based on these two journal entries, the balance in the labor cost account should be zero at the end of the period. This is due to the labor cost account is a temporary account that will be cleared at the end of the period.


